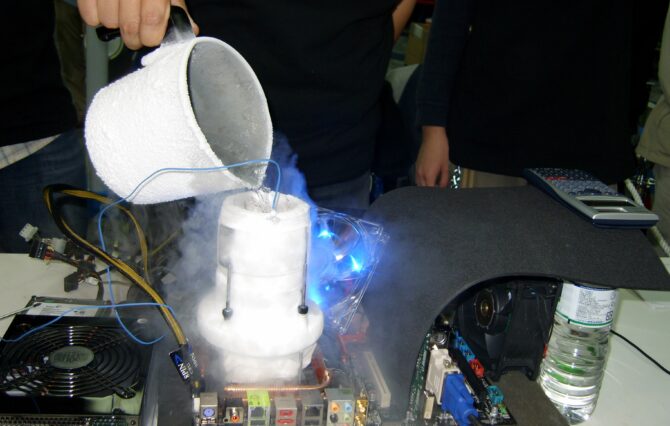
Overclocking Guide: A Beginners Handbook to Speed 🔥
So, you’ve been browsing the internet and come across some people talking about this weird pc enthusiast hobby; Overclocking. You might be wondering what it is overclocking and how big the alleged performance gains from overclocking actually are.
Well, you have come to the right place to learn the basics about overclocking and come away with a basic understanding of what is going on.
Table of Contents
- 1 Basic Overclocking Terminology
- 2 What is Overclocking?
- 3 Is Overclocking my PC Safe?
- 4 Dealing with Extra Heat from Overclocking
- 5 What You Can Overclock
- 6 Confirming Overclock Stability
- 7 Checking Voltage, Multipliers and Tempreture in Windows
- 8 Andy’s Overclocking Tips for Newbies
- 9 Commonly Asked Questions (5)
I warn you, though, overclocking can be a slippery slope that soon leads to empty wallets, fewer presents for your partner and thoughts about how you can route your custom water cooling loop through your freezer.
Trust me. It happens – I’ve been there. 🤷🏼♂️

Without further ado; My name is Andy, and I will be your host for the next 10 minutes, where I will introduce you to the world of PC overclocking. If you want, you can follow me on Twitter for more content like this and other boring things.
This article was written to be an overview of overclocking basics for newbies. For that reason, I won’t be detailing how actually to overclock in this article. Instead, I will be covering overclocking theory.
Let’s get started, shall we?

Basic Overclocking Terminology
This small section is designed to help you understand common overclocking terminology and jargon used within the computer hardware community, in this article and on our blog in general.
- BSoD: The dreaded blue screen of death. Normally shown when Windows shits itself and decides enough is enough. Likely a sign you pushed you machine too hard.
- HSF: Heatsink and Fan. All OEM computers are shipped with one and is fitted to components such as CPU, GPU and on rare occasions North or South Bridge.
- Bios: The Bios or Basic Input/Output System is a system level operating system supplied by the motherboard manufacturer that allows you to control overclocking settings.
- Core Clock Speed: Used to describe a components clock speed which determines how fast it processes information.
- Core Voltage: The amount of voltage being delivered to a components core.
- VID : The amount of voltage being requested by the hardware.
- Stress Test: A program that places your computer under load to ensure your overclock is stable.
- Benchmark: A program that primarily benchmarks your computer against other results in a pool. Also used as overclock stability testing tools.
- Chipset: Installed on your motherboard, the chipset controls data-flow between components.
- Thermal Paste: A sticky substance used between components and cooling surfaces. It helps to form a consistent bond and promotes effective heat transfer.
- Liquid Metal: An enthusiast grade thermal paste made from liquid metal as the name suggest. Superiour heat transfer qualities however, not suitable for sub-zero cooling.
- AS5: Artic Silver 5. A legendary thermal paste in the overclocking community and a first choice for many enthusiasts. Yes, as the name suggests – does contain some silver.
What is Overclocking?

Overclocking is a hobby undertaken by computer hardware enthusiasts which simultaneously increases a pc components core clock speed, heat output and processing speed. Overclocked components commonly include a computer’s CPU, GPU and RAM but, it is possible to overclock other components as well, although not as frequent.
The performance benefits of overclocking your PC can be huge as well; Overclocking helps to squeeze extra performance out of your computer, allowing you to benefit from faster clock cycles and faster processing power without spending the money on more expensive computer hardware such as an Intel extreme edition CPU – In short? Everything runs faster – including your games (and crypto mining).
For this reason, PC overclocking is popular amongst computer enthusiasts, bitcoin miners, competitive benchmarkers and gamers who are looking for every ounce of performance they can get out of their computers.
Is Overclocking my PC Safe?
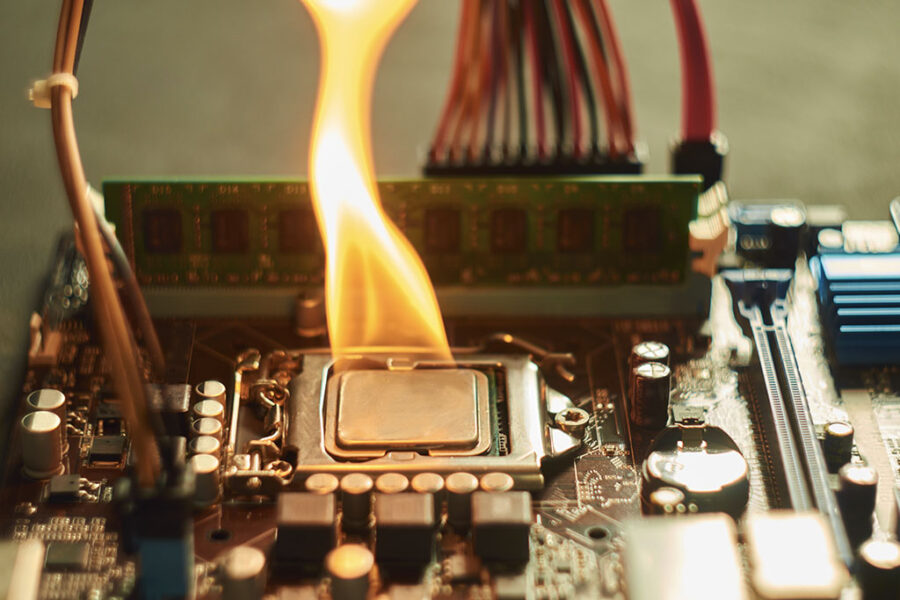
As with most things in life, there are risks to overclocking your computer. However, as long as you improve your computer’s cooling efficiency with cooling upgrades and remove the extra heat associated with overclocking components, there is no reason why it should damage your machine.
But, with risk kept firmly in mind please read the following overclocking disclaimer;
Overclocking shortens the life span of your computer hardware and can be fatal, resulting in dead components that cannot be returned or RMA’d. Do not attempt to overclock your machine if you are not 100% confident in changing your settings.
So, to summarize; Overclocking can be dangerous and result in fried components but, if you take care, learn the basics and keep your pc parts as cool as possible, you will avoid the pitfalls of overclocking and potentially dead pc parts in the process.
Don’t be put off though, hardware overclocking is an extremely rewarding hobby.
Dealing with Extra Heat from Overclocking

That OEM heatsink you’ve currently got installed is not going to cut it anymore, mi amigo.
Overclocking your computer increases heat. Unfortunately, there is nothing you can do to stop it either, especially if you are determined to get more raw performance and speed out of your machine. All you can do is increase your computer cooling efficiency by purchasing aftermarket cooling and funnelling excess heat away.
When overclocking your computer’s components, you will need to change several values to achieve your desired overclock, specifically, voltage. More voltage running through your pc components means a larger heat output to deal with. Because of these unwanted side effects, hardware overclockers often run aftermarket or extreme pc cooling solutions.
Now, I am not saying you will need to go out and buy a fully custom watercooling loop to start overclocking, but it will help without encouraging you. Especially if you’re the competitive type, who can’t get enough once they start – overclocking is highly addictive.
So, what types of cooling are good for overclocking?
Let’s find out.
Air Cooling
This option consists of a heatsink and a fan that attaches directly to your components. Some aftermarket air cooling solutions can sometimes come with heat pipes installed which are more effective at carrying away heat. With the correct airflow setup within your pc case and reasonable ambient room temperature, air cooling could be a solid choice for you.
Air cooling is uncomplicated and allows even the most clueless of overclockers to gain some extra MHz and benefit from the overclocking gains to be had.
Water Cooling
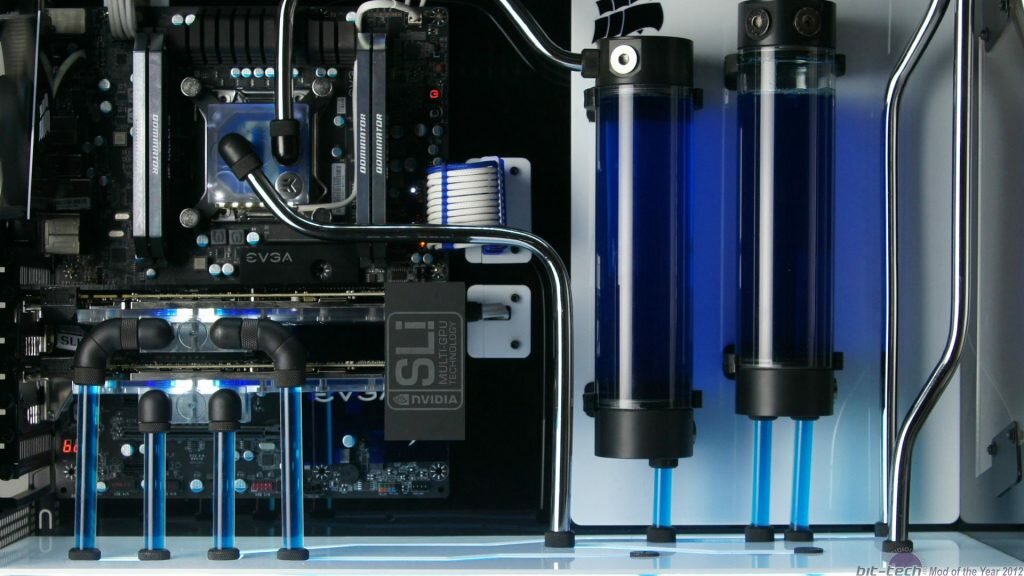

Water cooling is a form of extreme pc cooling. It’s a highly effective way of cooling your overclocked components. Water cooling can come in two formats; Custom or premade.
All-in-one units are rarely worth the investment if you want to push extreme overclocks. On most occasions, they are not much better than a good air cooling setup. Custom water cooling your PC is another beast, though. A well planned and built custom loop is where water excels at cooling your components.
Bonus: Beginners Guide to Watercooling
Liquid Nitrogen (LN2) & Dry Ice
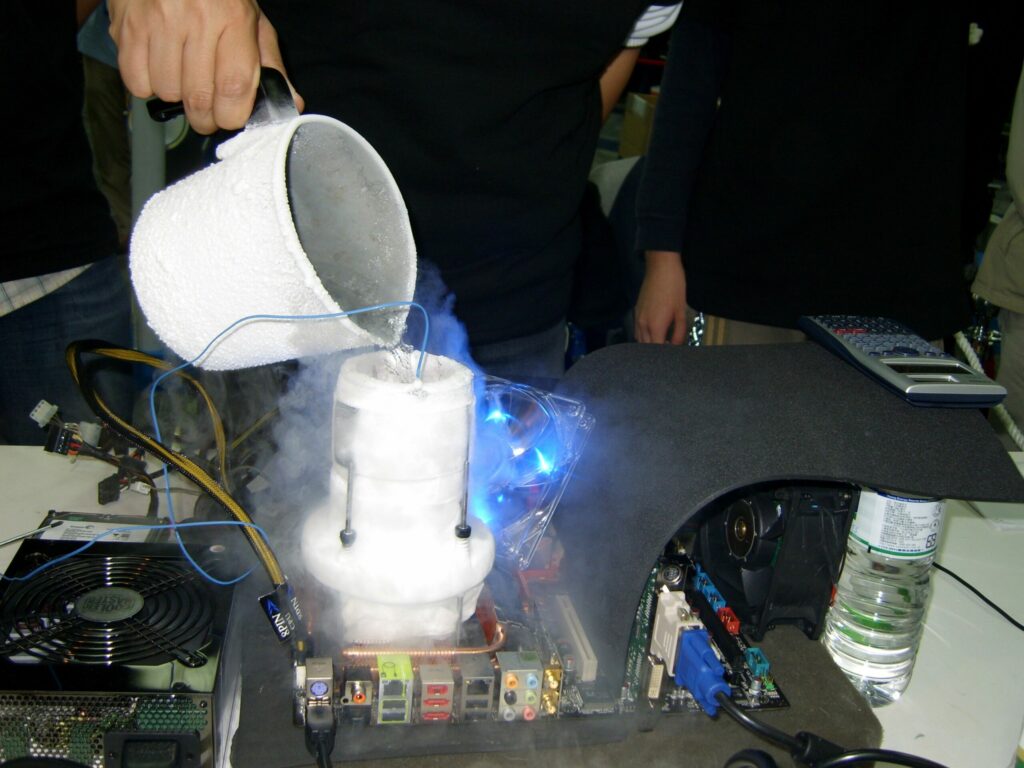

Liquid Nitrogen (LN2) & Dry Ice and reserved for extreme overclocking. It’s impossible to run LN2 or CO2 ice 24/7 due to the constant attention this form of extreme pc cooling demands from the owner.
This type of sub-zero pc cooling is normally reserved for and used by die-hard enthusiasts who normally hunt world records or want to push their computer’s hardware to the absolute limits – even if it is only for a few minutes.
What You Can Overclock
There are various components in your computer that you can overclock (and some that you can’t) that can be modified to run faster than advertised by the manufacturer.
In this section of my overclocking guide for absolute beginners, we will look at the most commonly overclocked pc components.
Remember, this is a guide for beginners. So, remember that when you are sat scratching your head and wondering why I left stuff out like monitor refresh rate overclocking, PCIe overclocking and others out, their practices are generally reserved for advanced overclocking guides.
CPU Overclocking
Most people start overclocking with their CPU. No special software is required as it is recommended to overclock your CPU via your motherboard BIOS due to the low-level control it provides over your system’s hardware. While it is possible to overclock your computer’s CPU with free desktop overclocking tools, it is not advice you will hear too often from us in the overclocking community.
Desktop-based overclocking with tools can be extremely buggy and doesn’t teach you the fundamentals of overclocking.
Due to stability issues, I would only recommend overclocking your CPU via the BIOS.
GPU Overclocking
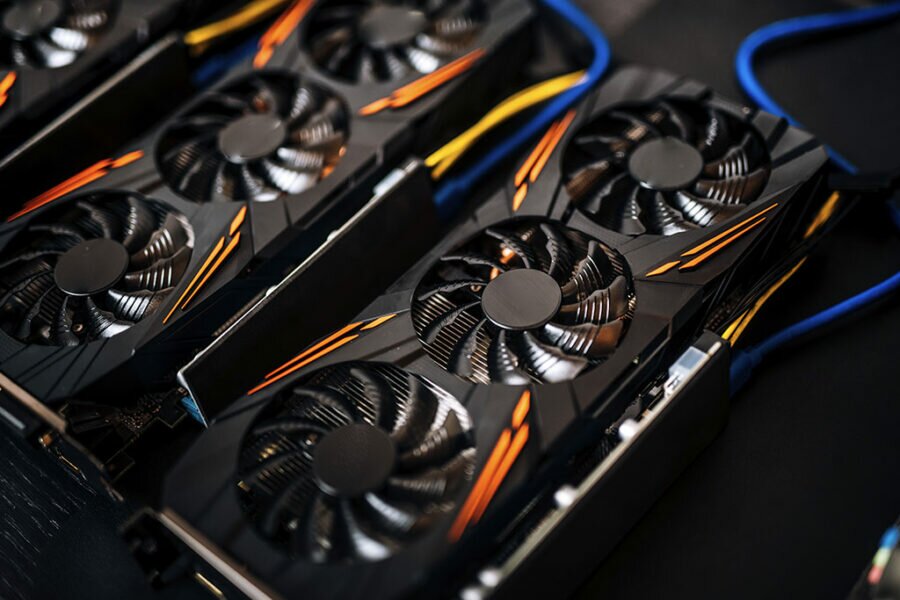

We overclock our GPU’s to get more performance without breaking wallets. GPU overclocking will increase your FPS in games, increase hash rates when mining crypto or training neural networks. Performance gains can sometimes be huge depending on the application using your hardware.
There are no BIOS-based overclocking screens like with CPU overclocking. In most cases (I say most because I am looking at you miners with your custom bios software under volting your GPU cards), GPU overclocking is performed via desktop software for your computer.
RAM Overclocking

RAM overclocking can be confusing and is almost exclusively conducted via the motherboard BIOS once again. I say that RAM overclocking is complicated because it’s more than just increasing the frequency or ‘clock’ of your RAM modules.
RAM Timings play a big part when overclocking your RAM and will provide a larger performance increase over increase the bandwidth capabilities of your modules.
Confirming Overclock Stability
System stability is the pinnacle of overclocking, and stress testing ensures we achieve that. Ok, so you might be able to turn on, post your system and boot into Windows but, if you cannot run any verifiable tests before it crashes to a blue screen of death (BSOD), then, officially, the overclock never happened.
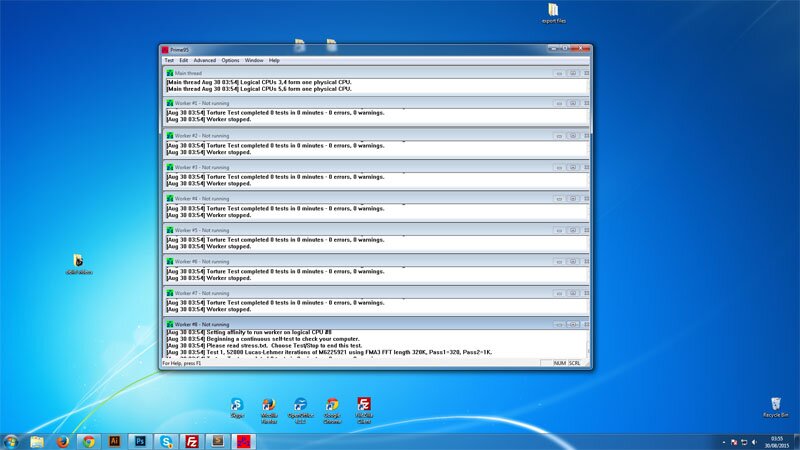
You see, without verification from one of the many free overclocking tools and benchmarking programs at your disposal, you cannot validate that your computer system is stable, nor can you share your results with the world.
Overclock Stability Testing Overview
- CPU: Stress testing your CPU is normally done in Windows with not just one but a variety of programs. The key to stress testing your CPU is making sure it is placed under a sufficiently high load. I always start with 3DMark to warm things up and follow up with Prime95 and optimal settings
- GPU: 3DMark really is a great program that places your entire system under considerable load. The goal is to push your GPU to its limits and help show up the cracks. If you can manage 5 back to back rounds of 3DMark with everything maxed out – you can bet you’re stable. Backing the claim up with an intense gaming session will help validate GPU overclock stability.
- RAM: There are lots of way to stress test your RAM. Some involve command-line programs that must boot on startup, but my favourite method is using Prime95 and SuperPI. Calculations are memory intensive, so it’s important to make sure you max out the settings and then run several iterations.
As you see, how you decide to test your components overclock stability will depend largely on the part being tested at the time.
Leaving instability can and will arise if you have an intense gaming session, mining crypto, encoding video edits or any other intensive tasks. Ultimately, you will only lessen the life span of your components.
Checking Voltage, Multipliers and Tempreture in Windows
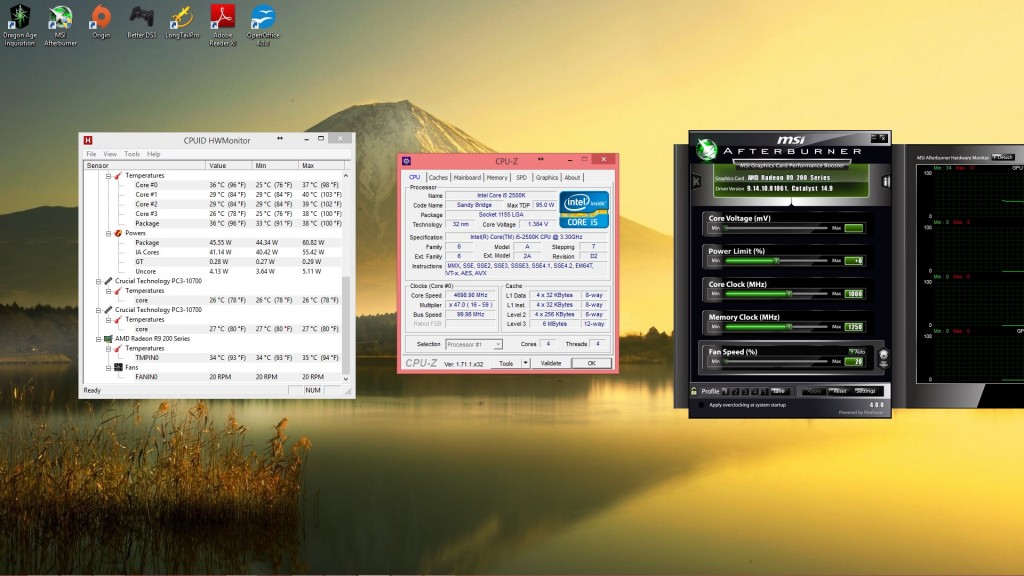
When stress testing and benchmarking your computer, to validate your system is indeed stable, you need to be able to monitor vital system metrics directly from your Windows desktop.
Some key information overclockers need is;
- Voltage A real-time view of the voltage being delivered to your CPU, GPU, RAM, Motherboard and even Hard drives
- Core Clock Speed A real-time view of the core clock speed or ‘frequency’ of your CPU, GPU or RAM
- Power Supply Load A real-time view of the power supply load. Displays +3.3v, +5v and +12v rails.
- Load A real-time view of your components system load
While there are many hardware monitoring programs available to download on the internet, My favourite (and free program) is HWmonitor. HWmonitor enables you to monitor, in real-time, key details about your system to ensure that everything is running as it should.
Andy’s Overclocking Tips for Newbies
So I was thinking that after reading almost 3000 words of boring overclocking theory that you might be feeling a little overwhelmed, am I right?
I thought, right. So, I would put together some overclocking tips (and some secret sauce). Small things I have learned and picked up over the years. Hopefully, it should help you make sense of everything and how you can start overclocking yourself.
1. Learn About Max TDP
Every component and PC part of your computer has thermal limits. Limits to the amount of heat they can tolerate before melting into the motherboard and crapping out.
Maximum Thermal Design Power or Max TDP for short refers to the maximum amount of heat your chip is expected to be able to handle. Max TDP is different for every component or chip inside your computer.
Do you need a quick ELI5? Max TDP dictates the maximum amount of voltage a specific pc part can handle. This value varies depending on the cooling you have.
For example, components being cooled with water will handle more voltage than pc components being cooled by air. This is because the cooler your components are, the more voltage you can supply to stabilise your overclocks.
2. Overclock CPU from BIOS
Many programs offer the ability to modify your processor’s multiplier directly from your Windows desktop. However, while it’s highly convenient for quickly overclocking your computer, stability is a major concern.
Overclocking your CPU from the BIOS is recommended by almost all seasoned overclockers. Experts will tell you a whole list of benefits, but voltage delivery and stability are the main concerns.
Your components are susceptible to voltage changes. It’s why you are recommended to remove static and ground yourself when building or dealing with any computer hardware. It’s argued that sudden spikes in voltage caused by desktop overclocking may damage the hardware. However, findings are inconclusive, with no verifiable data at this time though. So I don’t fancy taking the risk.
3. Heat Output Will Make or Break Overclock Attempts
I mentioned earlier that overclocking increases your pc parts heat output. So if you decide to start overclocking, heat will become your arch-nemesis.
Laws of thermodynamics state that you will never be able to get your pc cooled below ambient temperature without some outside help – did someone mention a dewar of LN2?
Take time to ensure you’re following pc case airflow essentials and your room is getting an adequate amount of fresh airflow. If you have air conditioning? Turn the temperature control right down.
The cooler you can get your components, the more voltage you can push through them, meaning you can achieve higher overclocks.
Commonly Asked Questions (5)
Can I Overclock if I have a Stock HSF?
You can definitely overclock your CPU and GPU using the stock coolers but your gains will most likely be minimal as you will struggle with removing heat from your components efficiently.
Does Overclocking Shorten the Lifespan of Components?
While overclocking will definitely reduce the lifespan of your components. In the long run, the impact will be minimal however, if you don’t follow simple overclocking guidelines, you run the risk of frying your hardware.
Is Overclocking Worth It?
Overclocking is a risk-reward hobby and as such, should be approached with caution however if you are willing to accept the risks associated with overclocking, then yes, it is definitely worth it. The performance gains can sometimes be substantial depending on a few factors such as the components bin.
Do I Need Water Cooling to Overclock?
Contrary to popular belief and rumours circulating on forums; You don’t need water cooling to overclock your computer. In fact, with a good aftermarket air cooler, you can easily achieve some impressive performance gains without breaking the bank.
Does overclocking reduce CPU Lifespan
As with overclocking the rest of your pc components, overclocking your CPU will reduce it’s lifespan. The amount that its lifespan is reduced is dependant on a few factors but, as long as you keep your CPU cool, you won’t notice any difference at all. In fact, you will likely upgrade the machine before it stops working.